Research
At AiLearn Lab, our mission is to demystify artificial intelligence and bridge the gap between academic research and industrial application. We are committed to advancing the understanding and implementation of AI technologies across various domains. Our collaborations with industry partners are designed to apply cutting-edge AI research to real-world challenges, creating innovative solutions that propel both scientific and practical advancements. By integrating academic insights with industry expertise, we aim to foster transformative technologies that can scale from the lab to the field, enhancing both economic and societal well-being.
On going research program
Review:
Our primary work focuses on utilizing new algorithms to train neural networks. Over the past decade, we have successfully employed non-iterative learning methods to train hundreds of feedforward neural networks, thousands to tens of thousands of autoencoders, and deep convolutional neural networks with up to 50 million parameters. For instance, our latest theory enabled us to successfully train a 101-layer ResNet using our novel learning methods, enhancing learning effectiveness and generalization performance.
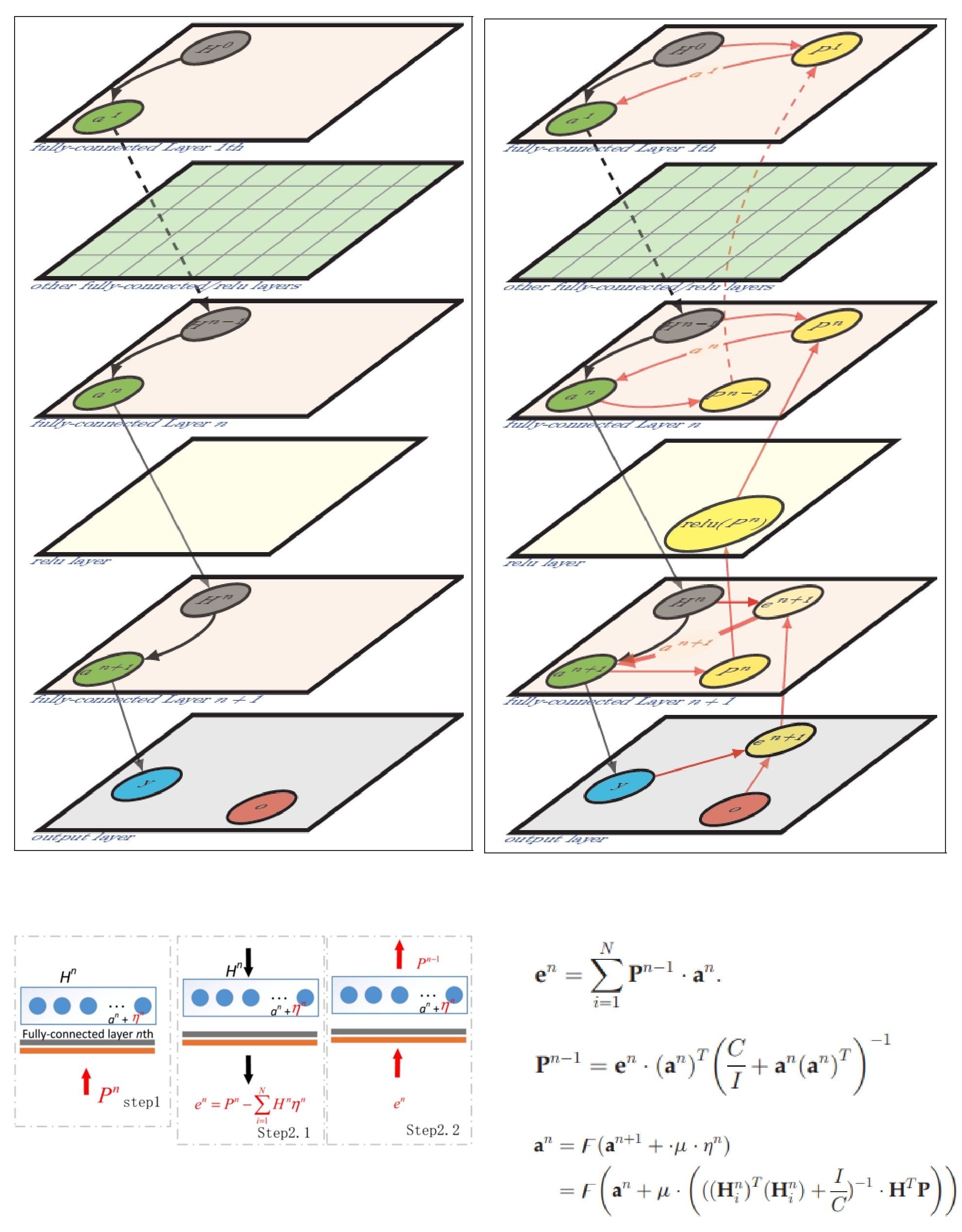
Method:
We utilize Moore-Penrose matrix inversion to train all neurons in neural networks. As a result, we had to redesign the entire error backpropagation process and the parameter update mechanisms for each neuron layer. We also developed specific algorithms for different types of neural layers, including fully connected layers, ReLU layers, normalization layers, softmax layers, addition layers, and others.
Result:
Our method demonstrates that, with less than 50 million parameters, the proposed algorithm can significantly enhance performance and learning speed. Additionally, at the same performance level, the new training method can substantially reduce the number of parameters in the neural network. This leads to more efficient models that require less computational resources. Future Direction:
In the future, we aim to apply this method to train large language models (LLMs) such as BERT, GPT, and Llama. By leveraging our novel training algorithms, we hope to improve the efficiency and performance of these models. This could lead to faster training times,
reduced computational costs, and enhanced generalization capabilities in natural language processing tasks.
On going applied projects
Towards Trustworthy AI that Aids Radiologists in Mammogram Analysis: An Interdisciplinary Approach using AI, Healthcare Data Science, and Ethics in Technology
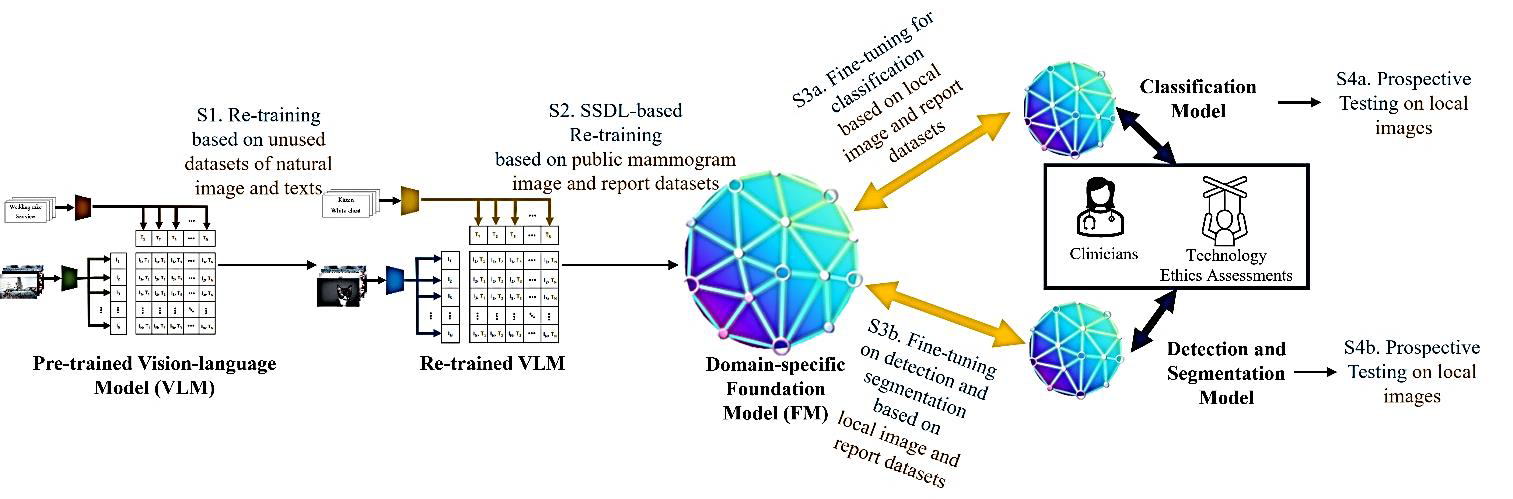
Project Overview: The project aims to develop a novel AI system to assist radiologists in interpreting mammograms (MGs) by addressing technical issues such as the lack of large-scale datasets, label variance, and imbalance caused by the low prevalence of abnormal findings in MGs. The goal is to enhance the generalizability, multimodality, and clinical workflow applicability of AI models, ultimately building trust among radiologists and integrating ethical considerations into AI design.
Methods: The project uses a variety of public imaging and text datasets from different countries to create a domain-adapted MG-specific foundation model (FM) from a retrained Vision-Language Model (VLM). The methodology involves generating text explanations for visual features and highlighting important visual regions, followed by several assessments with radiologists to gather feedback and labels of trust, error severity, and necessary actions. Ethical assessments will include evaluating biases based on various demographic and clinical factors. Additionally, prospective screening data from a local Canadian institution will be collected to validate the model.
Results: The expected results include the development of four novel AI models, with two specifically incorporating ethical feedback. The project aims to achieve prospective validation results on local pilot data, demonstrating the generalizability and ethical implications of the models. The outcomes will also include reusable AI models for related tasks and insights into the practical challenges and solutions for AI integration into clinical workflows.
Future Direction: Future directions involve further refining the AI models based on continuous feedback from radiologists and ethical assessments. The project will explore scenarios for updating the models and address concerns about overdiagnosis, especially for disadvantaged groups. The long-term goal is to expand the capacity for routine MG screening in Canada, potentially alleviating the burden on radiologists due to increased screening needs. The successful integration of AI tools in clinical practice could have significant economic and clinical impacts.
Force Prediction of Gust Impact on Buildings with Time-Series Transformer Models
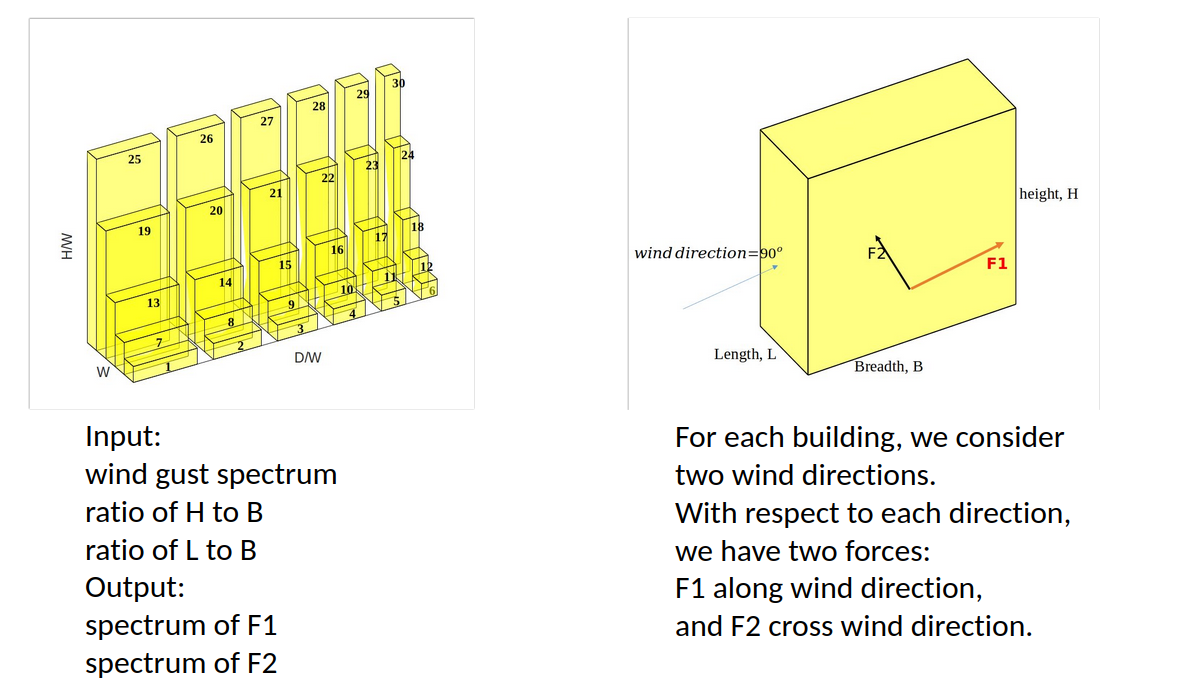
Project Overview: The wind energy project focuses on understanding and predicting the effects of wind on buildings by analyzing the wind forces at various points on a building’s surface. This is a complex regression problem where the goal is to predict the wind’s impact on a building based on various input features, such as the building’s dimensions, the angle of the roof, the angle of the wind hitting the roof, and the fluctuation of the wind. The output is a detailed map of wind forces on different coordinate points of the building, helping us understand how wind energy disperses and exerts pressure across the building’s surface.
Data and Methodology: The dataset we used contains input features related to the building’s shape and wind conditions. Specifically, the inputs include the building’s length, width, and height dimensions, the angle of the roof, the angle at which the wind hits the roof, and the degree of wind fluctuation. The output data consists of wind force measurements at multiple coordinate points on the building’s roof. We worked with a sample data set containing records of wind force variations at 335 coordinate points on the roof, with a total of 49,792 measurements. This extensive data provides a detailed picture of how wind interacts with the building. Our task was to train a model to predict the forces at these coordinate points, which involve 20x20 pixel images for each label, representing average, maximum, and minimum wind forces at each point.
Challenges and Solutions: One of the primary challenges we encountered was capturing the nonlinear relationships and periodicity of wind forces. The interaction between wind and the building’s structure is complex, requiring a model capable of understanding intricate dynamics. We addressed this by exploring advanced regression models, including neural networks that can handle multivariate inputs and learn from the spatial-temporal dynamics of the data.
Results and Future Directions: Our initial results have been promising, with the model effectively predicting the wind forces at various points on the building’s surface under given conditions. As we continue to refine our model, the goal is to improve its predictive accuracy and robustness, enabling it to handle more complex scenarios and a wider range of building structures.
AI-Powered Rental Property Management
Project Overview: Our project aims to develop an intelligent system for managing rental properties using AI, specifically large language models. The goal is to automate rent collection and property maintenance tasks to save time, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency. This project is part of the Mitacs-Accelerate program.
Project Objective: The primary goal of our project is to develop an intelligent rental property management system using large language models to automate rent collection and property maintenance processes. By leveraging advanced AI technologies, we aim to streamline these tasks, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. Our goal is to create a user-friendly, efficient system that works across various devices, improving overall property management for landlords and enhancing tenant satisfaction, particularly for those who face challenges with current systems. Through this project, we also seek to gain practical experience with AI deployment and system design, while addressing real-world challenges in the rental market.
Methods and Technologies Used: we are utilizing large language models to automate rent collection and property maintenance management. Our approach involves collecting and preprocessing relevant data, such as e-transfer confirmations and repair receipts, to train these AI models. We employ zero-shot learning to evaluate the initial performance of the models and fine-tune them as necessary to improve accuracy. Knowledge distillation techniques are used to optimize the models, making them smaller and more efficient for deployment.
AI-Assisted Real Estate Imaging
Project Overview: This innovative project harnesses AI’s power to revolutionize real estate imaging and analysis. It unfolds in multiple stages, each designed to enhance our understanding and capabilities in interpreting real estate imagery.
Stage 1: Floor Plan Detection
Objective: Develop a self-supervised learning model to accurately detect different areas within a home, starting with the floor plan.
Approach: We leverage cutting-edge AI models to detect and delineate distinct areas within home layouts, crucial for advanced feature recognition and property evaluation.
Stage 2: Luxury Level Assessment for Room Categorization [Read the published paper here].
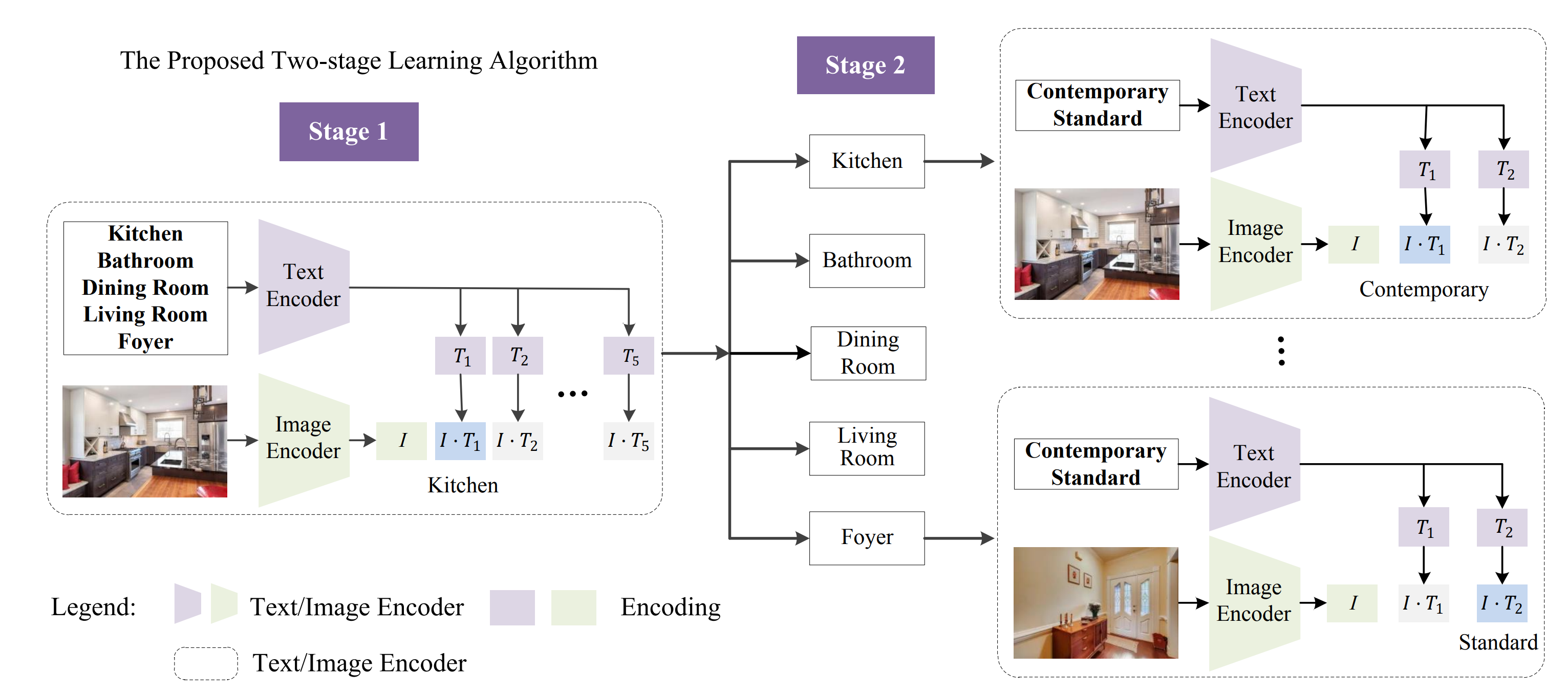
Objective: Classify the luxury level of rooms to enhance listing details and attract higher-value engagements.
Approach: Utilizing AI to classify rooms based on their luxury level, ensuring each property is marketed according to its true potential.
Finished projects
Recommendation System for Enhanced User Experience
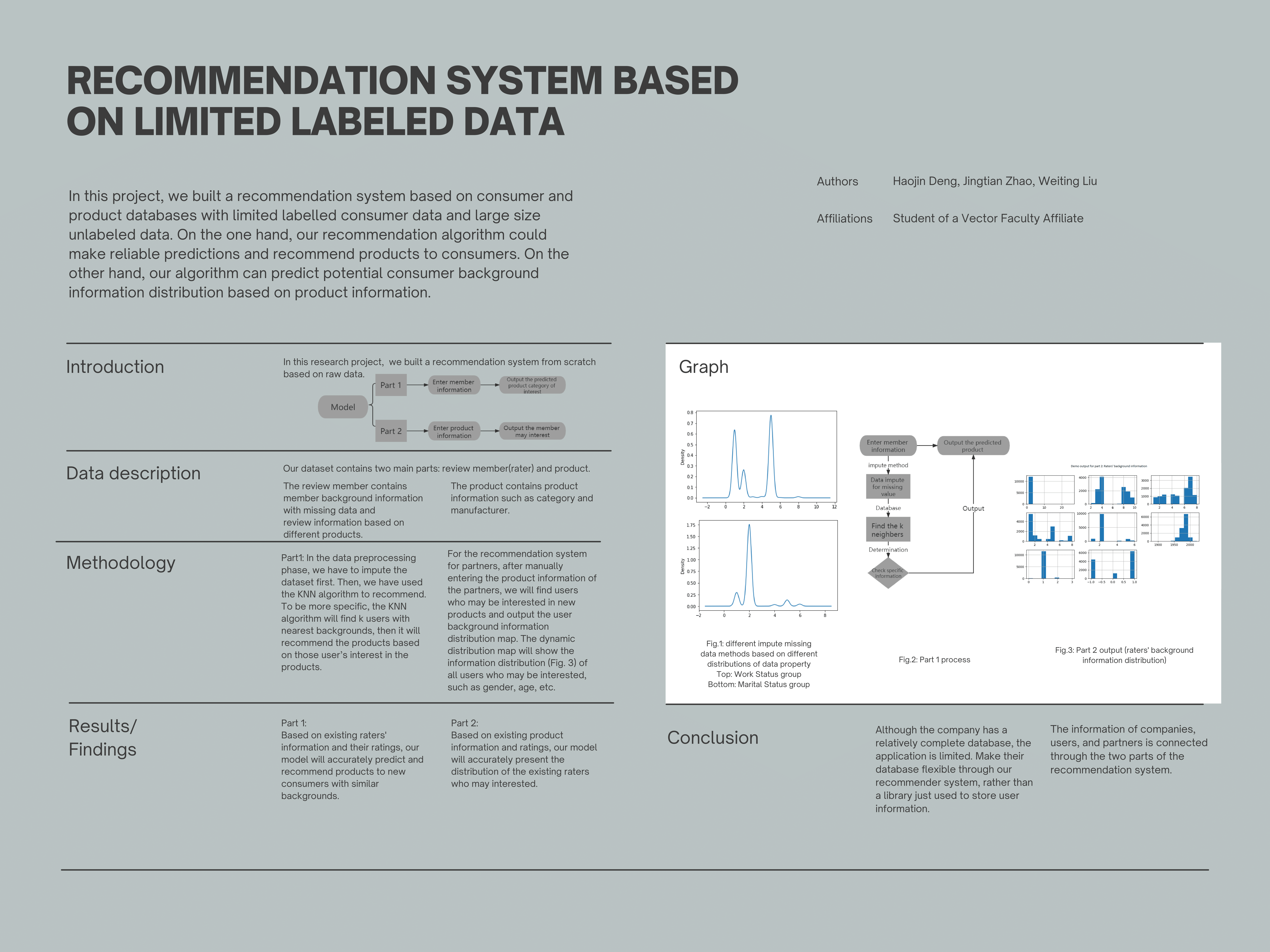 Project Overview: In this innovative project, our lab developed a two-part recommendation system aimed at significantly enhancing user experience by effectively utilizing big data and advanced machine learning techniques. The project was part of the Mitacs-Accelerate program and was carried out in close collaboration with industry partners.
Project Overview: In this innovative project, our lab developed a two-part recommendation system aimed at significantly enhancing user experience by effectively utilizing big data and advanced machine learning techniques. The project was part of the Mitacs-Accelerate program and was carried out in close collaboration with industry partners.
Objective: The primary goal was to construct a business-oriented user persona and predict consumer preferences more accurately. This system was designed to support marketing analysis and streamline product recommendations based on user data.
Methods and Technologies Used: We employed a variety of data processing techniques, including data augmentation, KD-trees, and the K-nearest neighbors algorithm, integrated with a user-friendly GUI developed in Python and backend processes handled via SQL. The system leveraged extensive data from user ratings and product information to predict consumer behavior and preferences.
Results: Our recommendation system successfully predicted and recommended products to new consumers with similar backgrounds to existing users. It also presented a dynamic distribution of user interests, allowing for targeted marketing strategies. The tool has been adopted by our industry partner, enhancing their capability to analyze market trends and personalize user interactions.
Future Directions: The project has set the stage for further enhancements to the recommendation algorithm, with potential improvements in computational efficiency and accuracy. Continued collaboration with industry partners will focus on refining these systems to adapt to evolving market needs and consumer data insights.